Understanding Sickle Cell Anemia: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Management
- by Diana Ndanu
- 05 January, 2025
- 0 Comments
- 5 Mins
No processed graphic yet.
.webp?locale=sheng)
No processed graphic yet.
Introduction
Sickle cell anemia is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, particularly those of African, Mediterranean, Indian, and Middle Eastern descent. Despite being a well-known genetic disorder, it’s often misunderstood. This article breaks down what sickle cell anemia is, its causes, signs, treatment options, and how it can be managed. Let’s dive in and raise awareness about this important health issue.
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
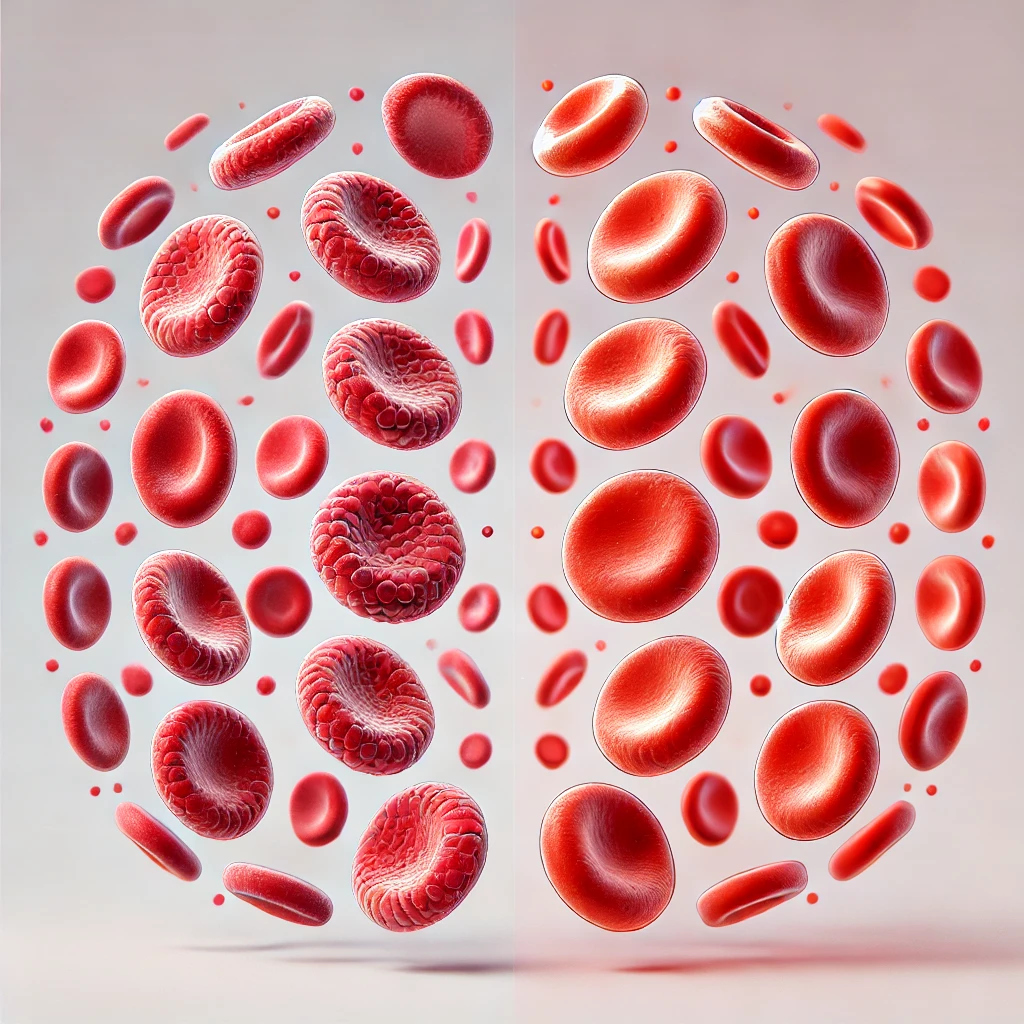
Sickle cell anemia (SCA) is a genetic blood disorder that affects hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells responsible for carrying oxygen throughout your body. In people with sickle cell anemia, the red blood cells are shaped like a crescent or “sickle” instead of the usual round shape.
These abnormally shaped cells are less flexible and can get stuck in blood vessels, blocking blood flow and causing pain and complications. They also die faster than normal cells, leading to anemia (a shortage of red blood cells).
What Causes Sickle Cell Anemia?
- Sickle cell anemia is an inherited condition, meaning it’s passed down from parents to their children through genes. To develop the disease, a person must inherit the sickle cell gene from both parents.
- If you inherit the sickle cell gene from one parent: You become a carrier (sickle cell trait) but typically don’t experience severe symptoms.
- If you inherit the gene from both parents: You develop sickle cell anemia.
- It’s caused by a mutation in the gene that tells your body how to make hemoglobin. This mutation results in abnormal hemoglobin known as hemoglobin S.
Signs and Symptoms of Sickle Cell Anemia
The symptoms of sickle cell anemia can vary from person to person. However, some of the most common signs include:
1. Anemia Symptoms
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Pale skin or yellowing of the eyes (jaundice)
2. Pain Episodes (Crises)
Sickle-shaped cells can block blood flow, causing intense pain that can last for hours or even days. This is one of the hallmark symptoms of the disease.
3. Swelling in Hands and Feet
This occurs due to blocked blood circulation.
4. Frequent Infections
The spleen, an organ that helps fight infections, may not function properly in people with sickle cell anemia, making them more susceptible to illnesses.
5. Delayed Growth and Puberty
Children with sickle cell anemia may grow slower due to a lack of red blood cells.
6. Vision Problems
Blocked blood vessels in the eyes can lead to vision complications.
Complications of Sickle Cell Anemia
Without proper management, sickle cell anemia can lead to severe complications, such as:
- Stroke
- Acute chest syndrome (a life-threatening lung condition)
- Organ damage
- Leg ulcers
- Gallstones
How is Sickle Cell Anemia Diagnosed?
Sickle cell anemia is often diagnosed at birth through a blood test as part of routine newborn screening. If you suspect you’re at risk or want to confirm your carrier status, a simple blood test called hemoglobin electrophoresis can identify sickle cell genes.
Treatment Options for Sickle Cell Anemia
While there’s no universal cure for sickle cell anemia, treatments focus on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life.
1. Medications
- Hydroxyurea: Reduces the frequency of pain crises and the need for blood transfusions.
- Pain Relievers: Used to manage pain episodes.
- Antibiotics: Often prescribed to prevent infections in children.
2. Blood Transfusions
Regular blood transfusions can reduce the risk of stroke and other complications by increasing the number of normal red blood cells in the body.
3. Bone Marrow Transplant (Stem Cell Transplant)
This is the only potential cure for sickle cell anemia but is usually reserved for severe cases. It requires a closely matched donor and comes with significant risks.
4. Emerging Treatments
Gene therapy is a promising area of research that aims to correct the genetic defect causing sickle cell anemia.
Managing Sickle Cell Anemia: Practical Tips for Daily Life
Living with sickle cell anemia can be challenging, but with the right strategies, you can lead a fulfilling life.
1. Stay Hydrated
- Dehydration can trigger a pain crisis, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
2. Avoid Extreme Temperatures
- Both extreme heat and cold can worsen symptoms, so dress appropriately for the weather.
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support overall health.
4. Prevent Infections
- Stay up to date on vaccinations.
- Wash your hands regularly.
- Seek medical attention promptly for signs of infection.
5. Manage Stress
- Stress can exacerbate symptoms. Consider relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
6. Regular Medical Check-Ups
- Frequent monitoring by a healthcare provider ensures timely intervention for complications.
Raising Awareness About Sickle Cell Anemia
Awareness is key to early diagnosis and better management. Communities, schools, and workplaces can contribute by:
- Hosting educational workshops.
- Encouraging genetic counseling for high-risk individuals.
- Supporting sickle cell research and funding initiatives.
The Future of Sickle Cell Anemia Treatment
With advances in medicine, the outlook for people with sickle cell anemia continues to improve. Research in gene editing, better medications, and innovative therapies offer hope for a brighter future.
Conclusion
Sickle cell anemia is a serious condition, but with proper care and awareness, individuals can manage symptoms and lead healthy lives. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and exploring treatment options are vital steps toward better health.
If you or someone you love is affected by sickle cell anemia, don’t hesitate to seek professional advice. Together, we can break the stigma, spread awareness, and support ongoing research to find a cure.
Got Your Own Experience? Share with us
Popular Categories
Mablogu Zinazobambwa Sana
Daily Newsletter
Get all the top stories from Blogs to keep track.



